
Aprende en Comunidad
Avalados por :





¡Acceso SAP S/4HANA desde $100!
Acceso a SAPExplorando la autorización OAuth 2.0 en SAP PO 7.5 SPS 16 con tipo de concesión de contraseña
- Creado 01/03/2024
- Modificado 01/03/2024
- 393 Vistas
0
Cargando...
This blog portrays the
OAuth2.0
authorization with grant type as ‘
Password
’.This is implemented in SAP PO 7.5 SPS 16 Patch 15. Lets take a tour into the Standard solution in elucidate with latest updates. ? Over to content below:
OAuth (Open Authorization) is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for Internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords.
OAuth introduces an authorization layer separating the role of the client from that of the resource owner.In OAuth, the client requests access to resources controlled by the resource owner and hosted by the resource server, and is issued a different set of credentials than those of the resource owner.The OAuth 2.0 authorization framework enables a third-party application to obtain limited access to an HTTP service:
(i) On behalf of a resource owner by orchestrating an approval interaction between the resource owner and the HTTP service (or)
(ii) by allowing the third-party application to obtain access on its own behalf.
The purpose of this blog is to explain OAuth 2.0 in SAP PO 7.5 SPS 16 with grant type as password. Regards to OAuth 2.0 solution worked with SAP in testing this solution and identifying bugs which resulted in correction notes published in the SAP marketplace to make this solution more robust to solve different OAuth 2.0 authentication integrations with varied systems/applications.
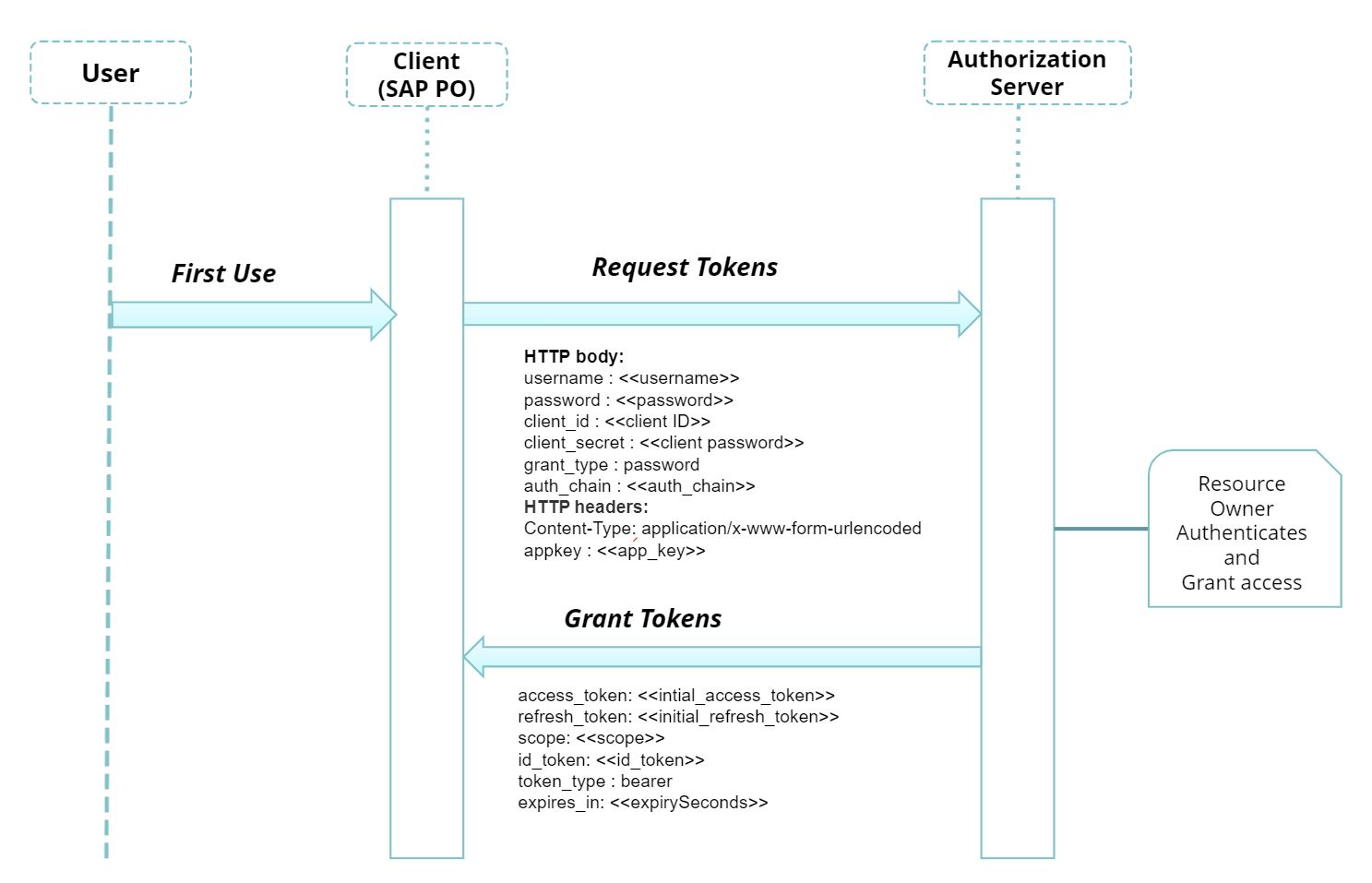
Below diagram depicts the Authorization Grant Flow to retrieve the access token and refresh token , POST a call to the authorization server. The client requests authorization from the resource owner and receives grant and then requests tokens by authenticating with the authorization server and presenting the grant. Authorization server validates, if valid then issues the initial access token and initial refresh token with access token expiry(lifetime in secs).
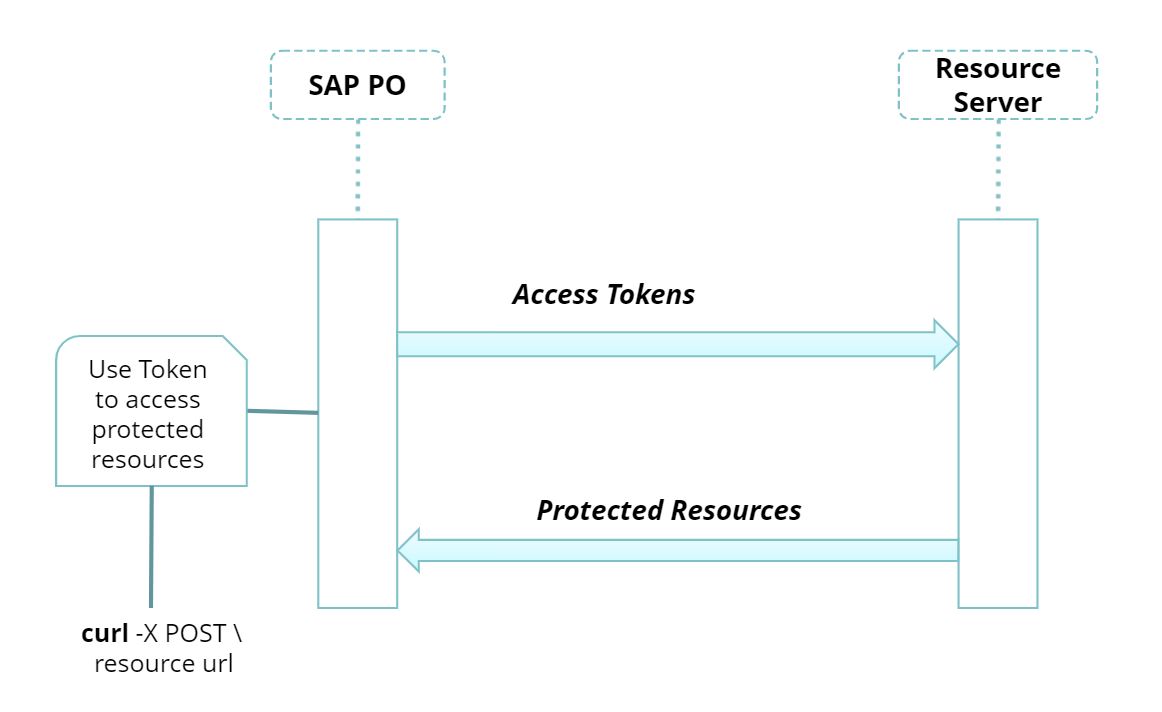
Below diagram elucidate that the client requests the protected resources from the resource server and authenticates by presenting the access token. The resource server validates the access token, and if valid, serves the requests and retrieves the response from the protected resources.
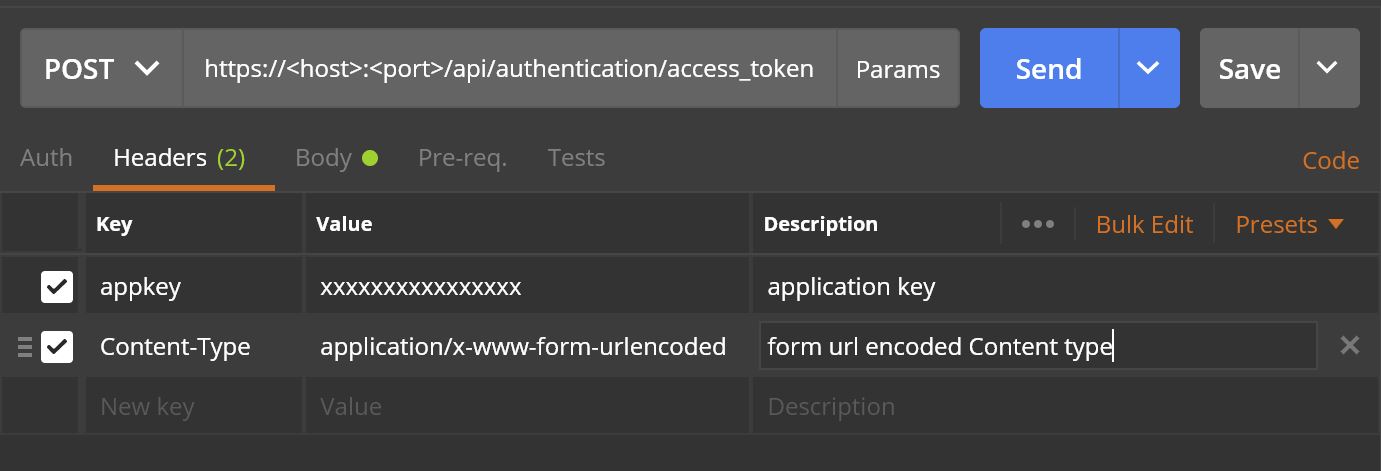
Before proceeding with the REST receiver communication channel configurations below is the Authorization server (which grants tokens) HTTP request header and HTTP request Body parameters look alike ?
HTTP Request Headers:
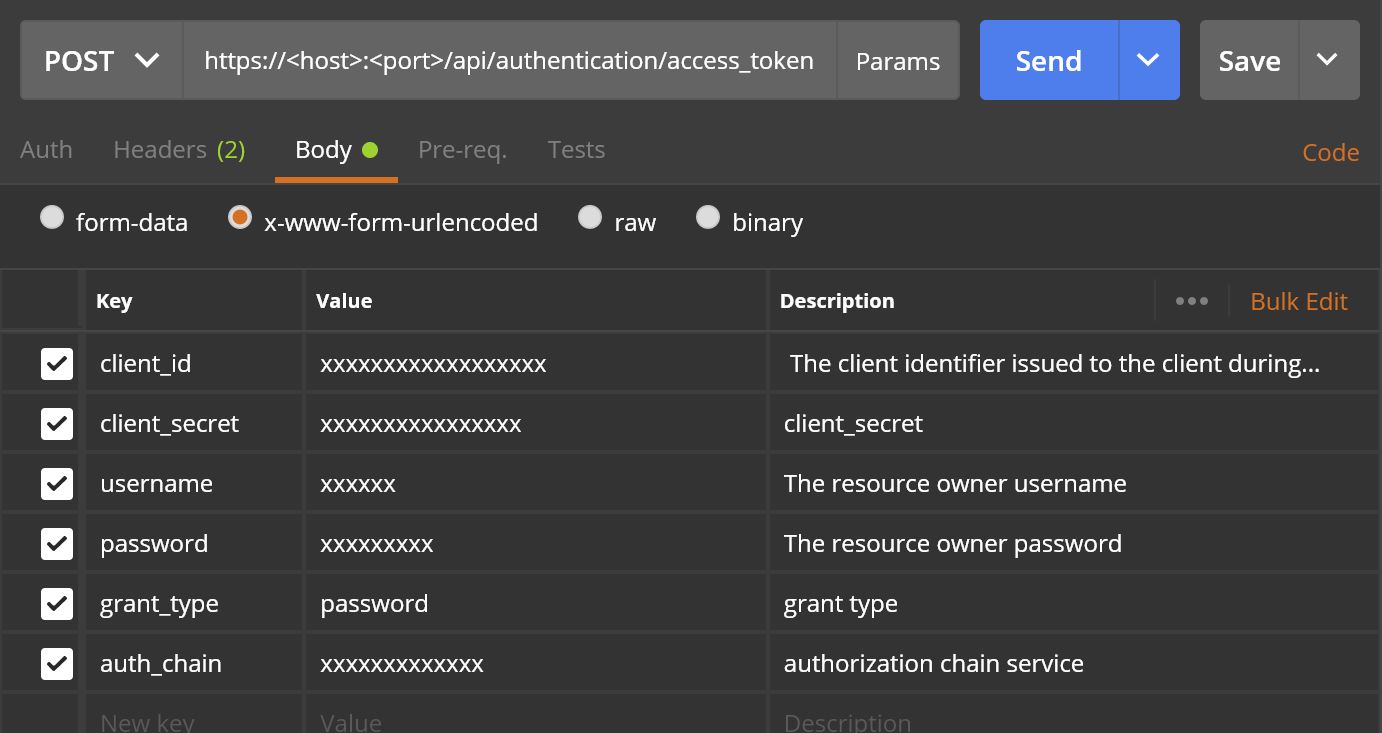
HTTP Request Body:
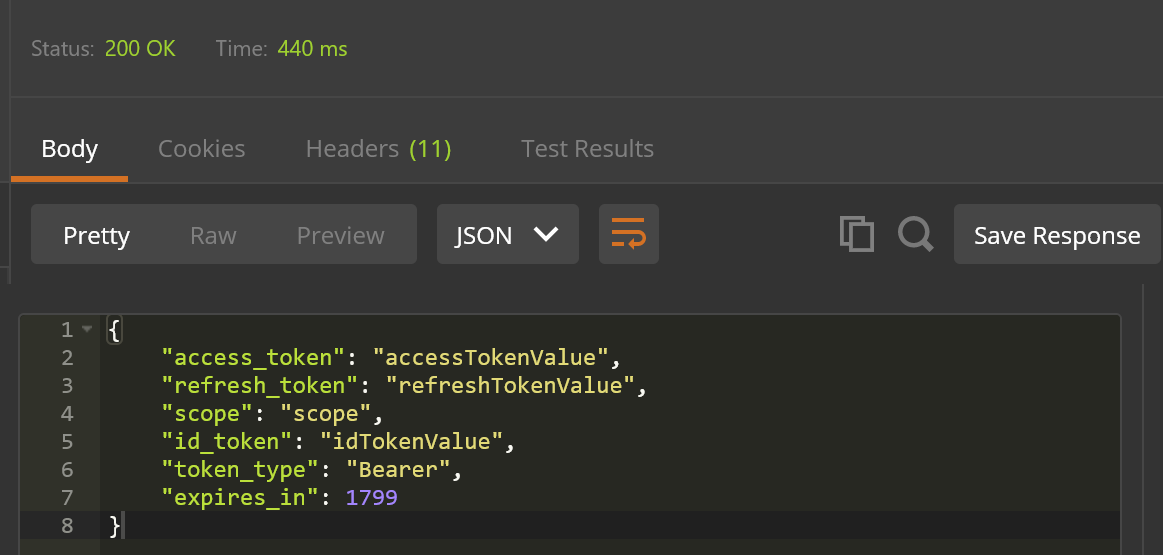
HTTP Response Body:
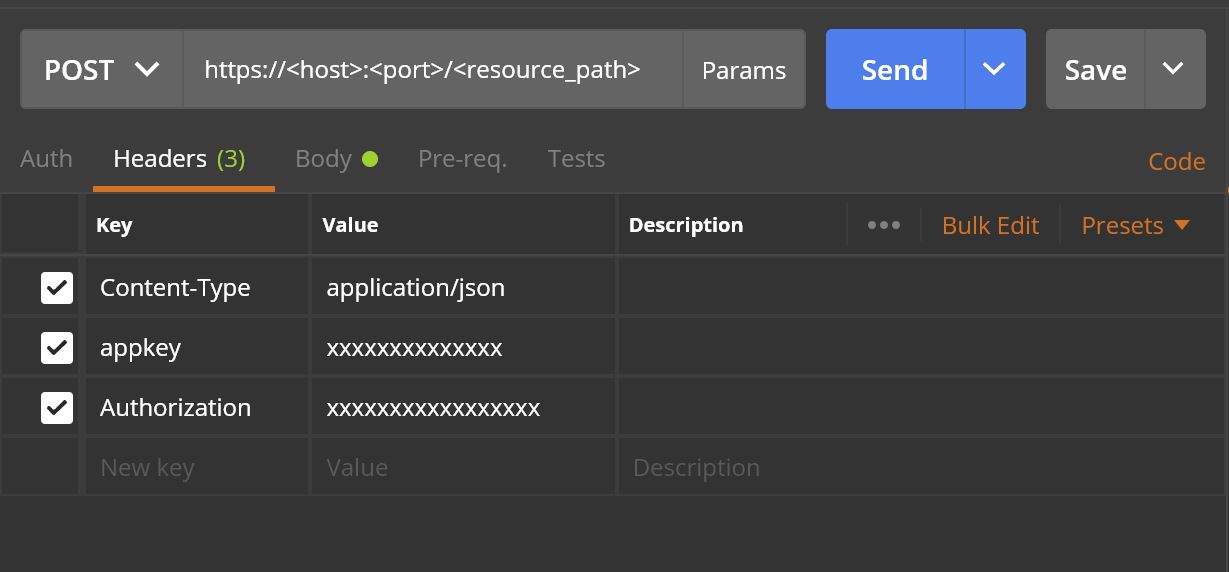
Below is the Resource server (which does the actual business call) HTTP request header and HTTP request Body parameters look alike
HTTP Request Headers:
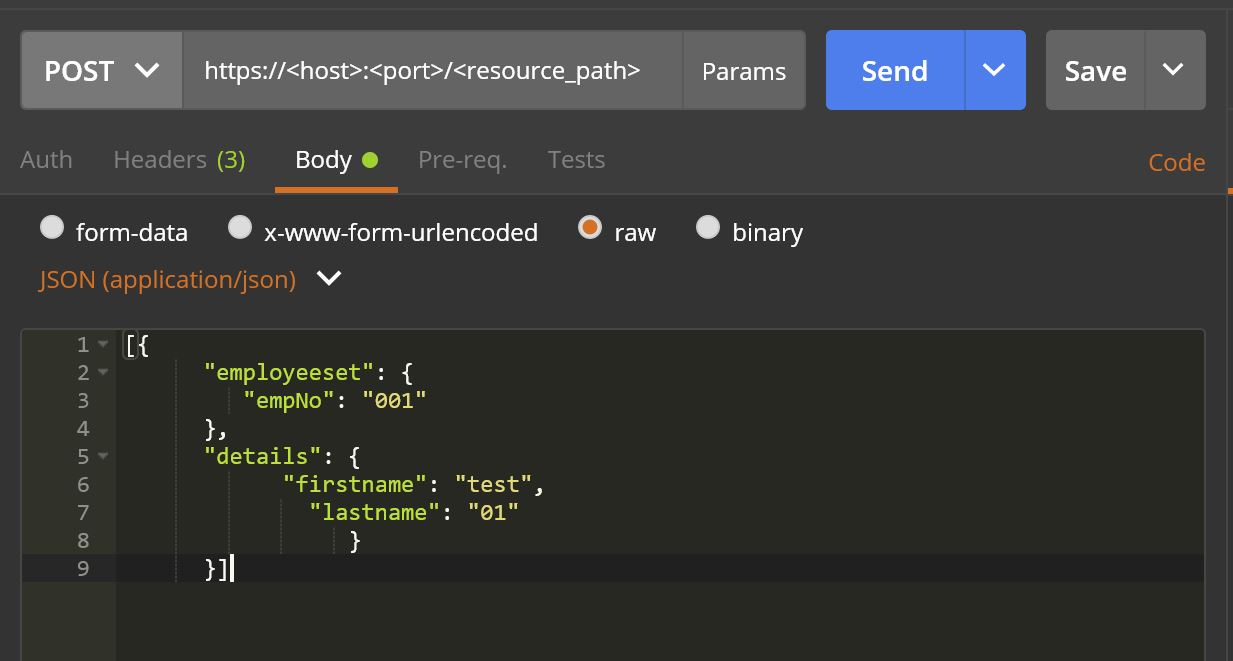
HTTP Request Body:
In the <
1. Introduction:
OAuth (Open Authorization) is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for Internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords.
OAuth introduces an authorization layer separating the role of the client from that of the resource owner.In OAuth, the client requests access to resources controlled by the resource owner and hosted by the resource server, and is issued a different set of credentials than those of the resource owner.The OAuth 2.0 authorization framework enables a third-party application to obtain limited access to an HTTP service:
(i) On behalf of a resource owner by orchestrating an approval interaction between the resource owner and the HTTP service (or)
(ii) by allowing the third-party application to obtain access on its own behalf.
2. Purpose:
The purpose of this blog is to explain OAuth 2.0 in SAP PO 7.5 SPS 16 with grant type as password. Regards to OAuth 2.0 solution worked with SAP in testing this solution and identifying bugs which resulted in correction notes published in the SAP marketplace to make this solution more robust to solve different OAuth 2.0 authentication integrations with varied systems/applications.
3. Authorization Code Grant flow:
Below diagram depicts the Authorization Grant Flow to retrieve the access token and refresh token , POST a call to the authorization server. The client requests authorization from the resource owner and receives grant and then requests tokens by authenticating with the authorization server and presenting the grant. Authorization server validates, if valid then issues the initial access token and initial refresh token with access token expiry(lifetime in secs).

Below diagram elucidate that the client requests the protected resources from the resource server and authenticates by presenting the access token. The resource server validates the access token, and if valid, serves the requests and retrieves the response from the protected resources.

4. SAP PO REST Adapter Configurations:
Before proceeding with the REST receiver communication channel configurations below is the Authorization server (which grants tokens) HTTP request header and HTTP request Body parameters look alike ?
HTTP Request Headers:

HTTP Request Body:

HTTP Response Body:

Below is the Resource server (which does the actual business call) HTTP request header and HTTP request Body parameters look alike
HTTP Request Headers:

HTTP Request Body:

In the <
Pedro Pascal
Se unió el 07/03/2018
Facebook
Twitter
Pinterest
Telegram
Linkedin
Whatsapp
Sin respuestas
 No hay respuestas para mostrar
Se el primero en responder
No hay respuestas para mostrar
Se el primero en responder
© 2026 Copyright. Todos los derechos reservados.
Desarrollado por Prime Institute
Hola ¿Puedo ayudarte?

